背景
我们有这样一个场景,有一个StudentDto类,还有一个StudentVo类
@Data
public class StudentDto {
private String id;
private String code;
private String sex;
private String userName;
}
@Data
public class StudentVo {
private String id;
private String name;
private String code;
private String age;
private String score;
private String sex;
}问题
“
如果我们知道
StudentVo的值,需要将StudentVo的属性拷贝到StudentDto中,你会怎么做。”
StudentVo的值如下
public StudentVo initVo() {
StudentVo studentVo = new StudentVo();
studentVo.setId("1");
studentVo.setAge("27");
studentVo.setName("Lvshen");
studentVo.setCode("001");
studentVo.setScore("100");
studentVo.setSex("male");
return studentVo;
}解决一
传统的解决方法,通过getter/setter方法将对应的属性值进行拷贝。
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() {
StudentVo studentVo = initVo();
StudentDto studentDto = new StudentDto();
studentDto.setCode(studentVo.getCode());
studentDto.setId(studentVo.getId());
studentDto.setSex(studentVo.getSex());
studentDto.setUserName(studentVo.getName());
System.out.println(studentDto);
}测试结果

看了上面的方法,你可能觉得不是很简单么。但如果属性非常多,比如有20多个。用上面的方法就会不美观,满屏的getter/setter方法,看着都眼花。
解决二
这时我们就可以使用BeanUtils.copyProperties方法啦,这里的BeanUtils是Spring的,而不是apache的。
@org.junit.Test
public void test2() {
StudentVo studentVo = initVo();
StudentDto studentDto = new StudentDto();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(studentVo,studentDto);
System.out.println(studentDto);
}测试结果

解决三(推荐)
我们还可以使用性能更优越的MapStruct,你可能没有听过这个东西。没关系,我们直接上代码。
MapStruct是一个可以生成类型安全的,高性能的且无依赖的 JavaBean 映射代码的注解处理器,可以在编译期生成对应的mapping,既没有BeanUtils等工具使用反射的性能问题,又免去了自己写映射代码的繁琐。
引入Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1.Final</version>
</dependency>实体拷贝
我们先编写一个StudentConverter类
@Mapper
public interface StudentConverter {
StudentConverter INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentConverter.class);
@Mappings(@Mapping(source = "name",target = "userName"))
StudentDto vo2dto(StudentVo vo);
}这里的@Mapper来源于org.mapstruct.Mapper,用来说明这是一个实体转换类接口。
@Mappings用来声明成员属性的映射,source = "name",target = "userName"即将StudentVo中name的值拷贝给StudentDto中的userName,如果属性名称相同,就不需要做这个映射。
测试结果
@org.junit.Test
public void test1() {
StudentVo studentVo = initVo();
StudentDto studentDto = StudentConverter.INSTANCE.vo2dto(studentVo);
System.out.println(studentDto);
}
List集合拷贝
你以为MapStruct只能进行实体之间的拷贝?NO,MapStruct还可以进行List之间的拷贝,这个就太牛了。
@Mapper
public interface StudentConverter {
StudentConverter INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentConverter.class);
@Mappings(@Mapping(source = "name",target = "userName"))
StudentDto vo2dto(StudentVo vo);
List<StudentDto> listVo2dto(List<StudentVo> vos);
}测试
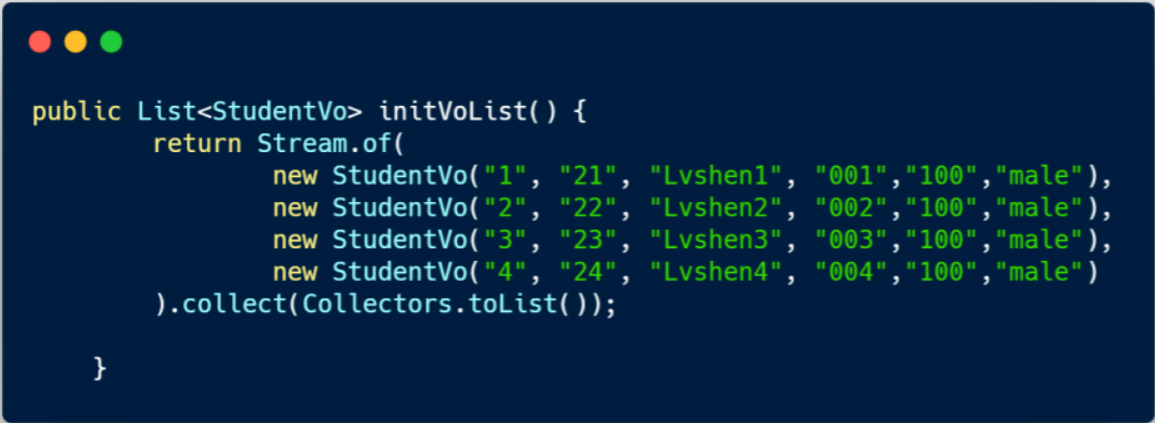
public void test() {
List<StudentVo> voList = initVoList();
List<StudentDto> studentDtos = StudentConverter.INSTANCE.listVo2dto(voList);
System.out.println(studentDtos);
}测试结果

当然MapStruct等功能远比你想象的要多,有兴趣的可以看看这篇文章
“
https://www.cnblogs.com/homejim/p/11313128.html
”
我为什么推荐使用MapStruct
市面上 BeanUtils底层是使用反射的,我们知道使用反射会影响性能。而且BeanUtils需要类型和名称都一样才会进行映射, 但在很多时候, 由于不同的团队之间使用的名词不一样, 还是需要很多的手动使用getter/setter。
于是MapStruct诞生了。
MapSturct 是一个生成类型安全, 高性能且无依赖的 JavaBean 映射代码的注解处理器(annotation processor)。
它有下面几个特点:
“
- 基于注解的处理器
- 可以自定义
JavaBean之间的属性映射 - 类型安全, 高性能, 无依赖性
”
编译之后会生成方法实现
实现的类、方法如下

该工具可以帮我们实现 JavaBean 之间的转换, 通过注解的方式。通过 MapStruct 来生成的代码, 其类似于人手写。速度上可以得到保证。